
Bridging the Data Knowledge Gap in the Digital Age
In the era of digital dominance, the world is awash with data. Yet, the ability to transform this wealth of information into actionable insights remains an intriguing paradox. In this blog post, we will explore the deeper nuances of the data knowledge gap, its far-reaching implications, and offer thought leadership on the best practices to bridge this divide.
The Macro Perspective: An Ocean of Data
The digital age has ushered in a data revolution, driven by various factors:
- Digital Transactions: The transition from physical to digital transactions has created a torrent of traceable data points across omni and multi-channel go-to-markets.
- IoT and Smart Devices: From the sensors in our homes to the data generated by our vehicles and storefronts, we are constantly immersed in data.
- Globalization and E-commerce: The interconnected nature of global markets generates a vast amount of data from diverse customer bases, each subject to varying regulatory requirements.
- Social Media: Every interaction on social platforms, be it tweets, shares, likes, or comments, contributes to the ever-expanding pool of data.
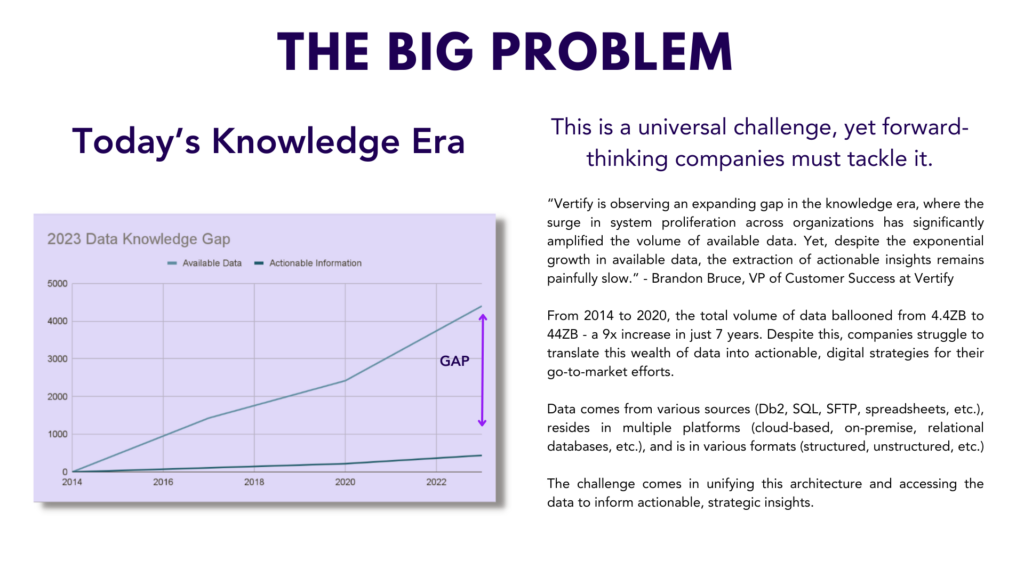
This abundance of data promises to revolutionize decision-making, market understanding, product development, automation, and monetization. However, it’s essential to recognize that the sheer volume of data doesn’t necessarily equate to its utility.
The Micro Perspective: Drowning in Numbers
Data may be the new oil, but refining it is where many organizations find themselves challenged. Several issues contribute to this dilemma:
- Overwhelming Volume: Despite improved storage capabilities, processing and analyzing terabytes of data daily remains a formidable task.
- Data Silos: Many organizations have data trapped in isolated systems or departments, making it inaccessible for holistic analysis.
- Quality Issues: Not all data is of the same quality. Distinguishing high-quality, actionable data from noise remains a significant challenge.
- Lack of Expertise: The shortage of data scientists and analytics experts means that even when organizations have the right tools, they often lack the manpower to utilize them effectively.
The Economic Story: Opportunity Cost
The inability to harness GTM data has significant economic implications:
- Lost Revenue: Companies miss out on potential revenue streams by failing to fully understand market dynamics or consumer behavior.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Both corporations and government entities suffer from operational inefficiencies that could be optimized through data-driven decision-making, resulting in substantial cost savings.
- Missed Innovation: Opportunities for new product development or policy initiatives based on data-driven insights are often lost due to the deluge of raw data and inaction in prioritizing a modern data layer.
The Way Forward: Best Practices and Thought Leadership
To bridge the data knowledge gap and unlock the true potential of the digital age’s most abundant resource, businesses and decision-makers should consider the following best practices:
- Investment in Education and Training:
- Establish data literacy programs within organizations to ensure that employees at all levels understand the value of data and how to use it effectively.
- Encourage continuous learning and upskilling in data science, AI, and analytics.
- Foster a culture of curiosity and experimentation, where employees are encouraged to explore data and ask questions.
- Robust Data Management Tools:
- Embrace modern, network-based architecture as the standard, providing access to an abstracted data layer for unified, transformed, managed, and analyzed data.
- Invest in advanced data analytics platforms and tools that facilitate data integration, cleansing, and visualization.
- Implement data governance practices to ensure data quality, privacy, and compliance.
- Collaboration:
- Break down data silos by promoting cross-functional teams and encouraging open communication and knowledge sharing.
- Democratize data access and provide domain-specific data sets to relevant teams and individuals, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Implement collaborative tools and platforms that enable seamless sharing and analysis of data.
- External Partnerships:
- Collaborate with external data experts or consultants to tap into specialized knowledge and experience.
- Consider strategic partnerships with data-focused companies to access cutting-edge technology and insights.
- Engage in industry collaborations and consortia to pool resources and address common data challenges.
Bringing It All Together
The data knowledge gap presents both challenges and unparalleled opportunities. With a concerted, strategic approach that involves investment in education, robust data management tools, collaboration, and external partnerships, we can bridge this gap and leverage the digital age’s vast data resources to drive productivity, innovation, and growth in businesses, industries, and societies. Embracing a data-first mindset and committing to ongoing learning and improvement will position organizations at the forefront of the data-driven revolution, enabling them to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
Vertify offers a broad suite of automated data integration solutions, complete with data cleaning tools and automated multidirectional integration between platforms, including multiple CRM integrations at scale. Vertify is the system of record for revenue operations professionals across the globe. Get started today, and see Vertify in action!